1. Classification Method
-
Definition: This is the simplest method, which categorizes suppliers based on performance factors, ranking them as "good," "neutral," or "poor." It provides a quick and straightforward way to evaluate suppliers.
-
How It Works: Key criteria such as product quality, delivery time, and service are classified and rated. The evaluation is often conducted by teams from purchasing, logistics, and production departments to determine the best supplier.
-
Advantages: Quick and cost-effective, suitable for preliminary evaluations.
-
Disadvantages: Lacks accuracy and relies heavily on subjective opinions.

2. Weighted Scoring Method
-
Definition: This widely used method assigns weights to evaluation criteria based on their importance to the business. Scores for each criterion are multiplied by their respective weights.
-
How It Works: Each supplier is evaluated on multiple criteria, with scores multiplied by pre-assigned weights. The total weighted score determines the supplier ranking. The supplier with the highest score is deemed the most suitable.
-
Advantages: Easy to implement, widely applicable, and provides accurate results.
-
Disadvantages: Requires time to develop appropriate scoring systems and weight assignments.
3. Cost Ratio Method
-
Definition: This method focuses on identifying cost elements that contribute to the total purchase cost. It helps businesses determine the most cost-effective supplier.
-
How It Works: All operational costs associated with procurement, such as product prices and internal operational expenses, are converted into cost ratios. The supplier with the lowest net cost is prioritized.
-
Advantages: Ensures cost efficiency in supplier selection.
-
Disadvantages: Focuses solely on cost, overlooking other factors like quality and service.
4. Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP)
-
Definition: AHP (The Analytical Hierarchy Process) is a decision-making tool that helps prioritize multiple criteria. It’s particularly useful for complex decisions involving both quantitative and qualitative factors.
-
How It Works: AHP involves three main steps:
- Determine the relative importance of each criterion.
- Measure how well each supplier meets each criterion.
- Synthesize the results to rank the suppliers.
-
Advantages: Handles complex problems, combines quantitative and qualitative criteria, and checks consistency in evaluations.
-
Disadvantages: Time-consuming due to the need for pairwise comparisons between criteria.
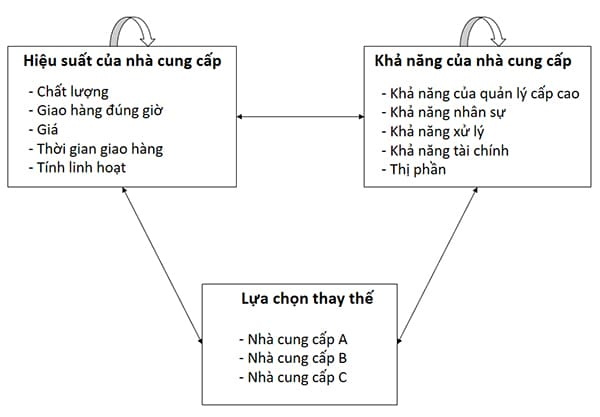
5. Analytic Network Process (ANP)
-
Definition: ANP (The Analytic Network Process) extends AHP by incorporating interdependencies among evaluation factors, making it suitable for more complex decision-making scenarios.
-
How It Works: ANP creates a network model, grouping related factors into clusters and identifying internal dependencies. For example, supplier performance and capabilities might be interconnected, affecting the final evaluation.
-
Advantages: More accurate than AHP, especially for complex scenarios with interdependent factors.
-
Disadvantages: Time-consuming and requires more effort due to complex comparisons.







AAdministratorsQTV
Welcome. Feel free to leave a comment, we will respond soon